Atrial Septal Defects (ASD): Symptoms, Underlying Causes, and Treatment Options
Introduction
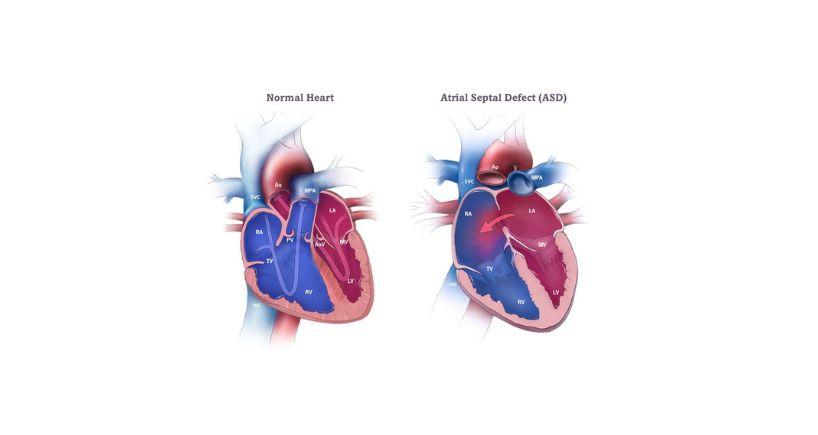
Atrial septum defects (ASDs) are characterised by abnormal holes in the atrial septum, a wall that separates the two heart chambers. This condition occurs in about 25% of children, and many cases of ASDs are only diagnosed in adulthood, delaying necessary treatment.
Causes of ASD
The development of the atrial septum begins around the fourth week of pregnancy and eventually closes as the division called septum primum grows from the top of the heart, dividing the right and left atria.
As this happens, another hole, the ostium secundum, forms due to cell death. Another layer, called the septum secundum, then grows next to the septum primum and partially covers the ostium secundum, leaving a gap known as the foramen ovale. In unborn babies, the foramen ovale allows oxygen-rich blood to bypass the lungs by circulating directly between the right and left atria. After birth, this hole usually closes as the baby starts breathing.
If the foramen ovale doesn’t close properly, it results in septal defects. The exact cause for this fault is not identified; however, certain factors such as family history, smoking, and alcohol abuse during pregnancy and infections such as rubella or lupus can be contributing factors.
Types of ASDs
- Ostium secundum defect: This occurs when the septum primum is too thin, or the septum secundum doesn’t close the ostium secundum.
- Ostium primum defect: This occurs when the septum primum doesn’t fully join with the endocardial cushions, leading to a connection between the atria and the heart’s valves.
- Sinus venosus defect: This occurs when a hole forms near where superior and inferior vena cava connect to the heart, allowing blood to flow between the right and left atria.
- Coronary sinus defect: This happens when the wall between the coronary sinus (a vessel that collects blood from the heart muscle) and the left atrium has a hole, allowing blood to mix between the atria.
These defects can cause improper blood flow and might need treatment if they are large or cause symptoms.
Symptoms
ASD symptoms are not evident at the time of birth. In some cases, the only indication may be an unusual sound in the heartbeat called a murmur, which your doctor can detect with a stethoscope.
In some cases, ASD may cause signs and symptoms in children, such as:
- Shortness of breath
- Feeling exhausted
- Underweight and delayed growth
- Throat and lung infections
- Irregular heartbeats
ASD symptoms in adults
Adults with ASD may also show signs and symptoms such as:
- Shortness of breath
- Arrhythmias
- Unable to exercise for long hours
- Collapsing
- Lung infections
Diagnosis
ASD can be diagnosed during a 20-week pregnancy, where the woman will be referred to further scans with specialists in foetal medicine and cardiology. Upon confirmation of diagnosis, the congenital heart disease specialist will guide the individual on managing the condition after birth. In certain cases, ASD may only be diagnosed after birth or later in childhood or adulthood. Some of the common tests used to diagnose ASD include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Echocardiogram
- Chest X-ray
- Cardiac CT scan
- Cardiac MRI
- Exercise testing
Treatment options
Treatment options for ASDs depend on the type and size of the defect, its impact on the functioning of the heart, and the presence of other comorbidities, such as pulmonary hypertension, valve diseases, or coronary artery disease. The doctor may advise repairing the hole in the heart. The two types of treatments recommended for ASDs include:
- Percutaneous (nonsurgical) repair of ASDs
This type of treatment is used to close the hole in the atrial septum using a device called septal occlude. The catheter is inserted into the large vein and carefully guided to the heart. The occlude is placed over the ASD. Over time, the patch will stay inside the heart and get covered by body tissue.
- Surgical repair of ASDs
Surgical repair involves closing the ASD with a tissue patch, often made from the body’s own pericardium (the membrane surrounding the heart). In some cases of secundum ASDs, the hole can be closed with sutures alone, without the need for a patch. This can be performed by advanced procedures such as robotic-assisted surgery or minimally invasive surgery.
Conclusion
ASDs are common congenital defects in the heart. Early detection and appropriate treatment are vital for preventing long-term issues. With advances in medical and surgical procedures, many ASDs can be effectively treated, offering improved outcomes and quality of life for those affected.
Popular Searches :
Hospitals: Cancer Hospital in Delhi | Best Heart Hospital in Delhi | Hospital in Amritsar | Hospital in Ludhiana | Hospitals in Mohali | Hospital in Faridabad | Hospitals in Gurgaon | Best Hospital in Jaipur | Hospitals in Greater Noida | Hospitals in Noida | Best Kidney Hospital in Kolkata | Best Hospital in Kolkata | Hospitals in Rajajinagar Bangalore | Hospitals in Richmond Road Bangalore | Hospitals in Nagarbhavi Bangalore | Hospital in Kalyan West | Hospitals in Mulund | Best Hospital in India | | Cardiology Hospital in India | Best Cancer Hospital in India | Best Cardiology Hospital in India | Best Oncology Hospital In India | Best Cancer Hospital in Delhi | Best Liver Transplant Hospital in India
Doctors: Dr. Rana Patir | Dr. Rajesh Benny | Dr. Rahul Bhargava | Dr. Jayant Arora | Dr. Anoop Misra | Dr. Manu Tiwari | Dr. Praveer Agarwal | Dr. Arup Ratan Dutta | Dr. Meenakshi Ahuja | Dr. Anoop Jhurani | Dr. Shivaji Basu | Dr. Subhash Jangid | Dr. Atul Mathur | Dr. Gurinder Bedi | Dr. Monika Wadhawan | Dr. Debasis Datta | Dr. Shrinivas Narayan | Dr. Praveen Gupta | Dr. Nitin Jha | Dr. Raghu Nagaraj | Dr. Ashok Seth | Dr. Sandeep Vaishya | Dr. Atul Mishra | Dr. Z S Meharwal | Dr. Ajay Bhalla | Dr. Atul Kumar Mittal | Dr. Arvind Kumar Khurana | Dr. Narayan Hulse | Dr. Samir Parikh | Dr. Amit Javed | Dr. Narayan Banerjee | Dr. Bimlesh Dhar Pandey | Dr. Arghya Chattopadhyay | Dr. G.R. Vijay Kumar | Dr Ashok Gupta | Dr. Gourdas Choudhuri | Dr. Sushrut Singh | Dr. N.C. Krishnamani | Dr. Atampreet Singh | Dr. Vivek Jawali | Dr. Sanjeev Gulati | Dr. Amite Pankaj Aggarwal | Dr. Ajay Kaul | Dr. Sunita Varma | Dr. Manoj Kumar Goel | Dr. R Muralidharan | Dr. Sushmita Roychowdhury | Dr. T.S. MAHANT | Dr. UDIPTA RAY | Dr. Aparna Jaswal | Dr. Ravul Jindal | Dr. Savyasachi Saxena | Dr. Ajay Kumar Kriplani | Dr. Nitesh Rohatgi | Dr. Anupam Jindal
Specialties: Heart Lung Transplant | Orthopedic | Cardiology Interventional | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | Onco Radiation | Neurosurgery | Interventional Cardiology | Gastroenterologist in Jaipur | Neuro Physician | Gynecologist in Kolkata | Best Neurologist in India | Liver Transfer | Best Cardiologist in Delhi



















