Calcium Deficiency in Children Symptoms, Causes and Remedies
Calcium is one of the many supplements that children need in order for the body to develop properly. In the body, we find vitamins used to create bones and teeth and support the muscular system and nerve impulses. However, most children end up having a calcium deficiency because they do not take enough calcium food products. This blog addresses the signs, sources and treatments of children’s calcium deficiency, offering specific recommendations for parents and child carers.
Symptoms of calcium deficiency
It should be noted that if calcium deficiency in children is not detected on time, it can become critical over the long term. Some common symptoms include:
- Osteoporosis and related fracture episodes: Lack of calcium leads to bone weakness. Thus, children are at high risk of breaking bones and experiencing bone pain.
- Delayed growth: One of the most important minerals to the skeletal system is calcium. A deficiency can, therefore, cause growth to be slowed or, developmentally, milestones to be missed.
- Dental issues: Children who have a low amount of calcium in their diet are likely to have rotten teeth, poorly developed tooth enamel or late tooth emergence.
- Muscle problems: Some of the signs common with low calcium levels include muscle cramps, spasms or weakness.
- Irritability and fatigue: Calcium influences the working of nerves and muscles. A deficiency of these vitamins can cause mood swings, irritability and persistent tiredness.
- Severe cases: Rickets or Osteoporosis: In severe cases, long-term deficit can result in rickets, a condition that affects bone hardness, rigidity and shape, or osteoporosis in adulthood.
Causes of calcium deficiency
It will also help prevent such problems due to faults in the body that lead to calcium deficiency. Some key factors include:
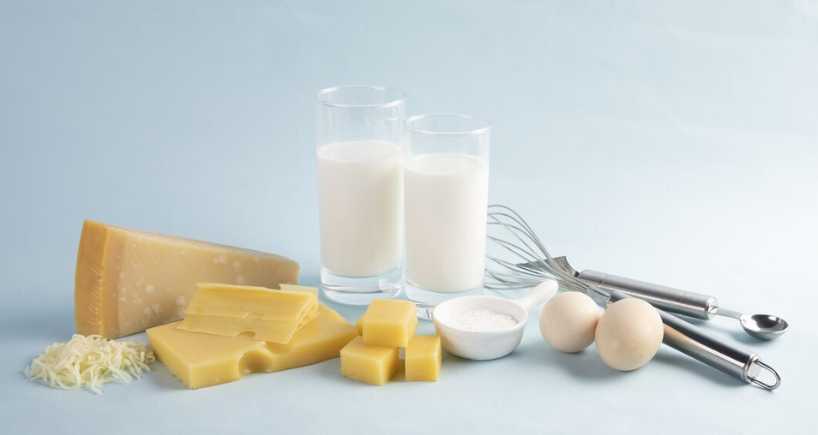
- Inadequate dietary intake: The major cause of deficiency is the inadequacy of calcium-containing foods such as dairy products, green leafy vegetables and calcium-fortified products.
- Vitamin D deficit: Vitamin D helps in calcium absorption. Children with no sun exposure or those with limited intake of vitamin D-rich food have low calcium levels.
- Lactose intolerance or dairy sensitivities: Those children with low dairy intolerance have a hard time meeting their calcium requirements.
- Medical conditions: Other conditions such as celiac disease, chronic kidney disease or hormonal imbalances affect calcium absorption and metabolism.
- Sodium and phosphate overload: Low intake of dairy products and increased consumption of salty foods, soft drinks and processed foods have been found to impair the ability of the body to absorb calcium.
- Growth spurts: In different developmental periods, the calcium requirement rises during periods of rapid growth in children. If it is not possible to meet these demands, then deficiencies can be present.
Remedies for calcium deficiency
Addressing calcium deficiency requires a multi-faceted approach, combining dietary, lifestyle and medical strategies:
It is therefore important to integrate calcium-containing foods: Ensure children consume a balanced diet including:
- Dairy products: Milk, cheese and yoghurt
- Non-dairy sources: Broccoli, kale, tofu, almonds and vitamin D-fortified cereals or plant-based milk
- Fish: Canned salmon or sardines of any type that contain bones
- Encourage vitamin D intake: Boost calcium absorption by:
- Consuming eggs, fish and other products that contain vitamin D
- Going outside to get at least 15 to 30 minutes of sunlight each day
- Using supplements if prescribed by a paediatrician
- Limit calcium inhibitors: Limit everyday consumption of sodas, processed foods and snacks that negatively impact calcium absorption.
- Investigate supplements if needed: Despite this recommendation not being so common, calcium may be prescribed for children who cannot get it from their food. Again, you should always consult your healthcare provider before taking supplements.
- Address underlying conditions: If conditions such as celiac disease or lactose intolerance are present, you should consult a doctor or dietitian to get the condition under control while ensuring adequate calcium intake.
Conclusion
Calcium deficiency is a condition that is easily preventable, but if it is not treated in children, it has the worst impact. This is because parents can easily identify the symptoms, and if they do not know the causes, they can be helped by physicians to take practical measures to ensure that their children grow healthy. These small positive changes in lifestyle would create a strong foundation for a calcium-rich diet that would hopefully yield strong bones and a brighter tomorrow.