Leaky Gut Syndrome: Definition, Symptoms, And Treatments
Introduction
Recently, the concept of “leaky gut syndrome” has gained attention in the health community. Leaky gut syndrome, described by increased intestinal permeability, is linked to gastrointestinal and extra-intestinal diseases. This condition is also associated with inflammatory bowel disease, irritable bowel syndrome, heart disease, obesity, diabetes, and celiac disease. Understanding the impact of dietary nutrients on barrier function is crucial for managing leaky gut-related disorders. This article delves into the intricacies of leaky gut syndrome, exploring its proposed causes, symptoms, available diagnostic tests, and potential treatment options.
What is Leaky Gut Syndrome?
Leaky gut syndrome is characterized by a compromised integrity of the intestinal lining, permitting the passage of substances like bacteria, toxins, and undigested food particles into the bloodstream. The breach within the gastrointestinal barrier has the potential to elicit different immune reactions and might play a role in the development of various health conditions.
Gut Microbiome and Its Role in Leaky Gut
The gut microbiome, comprising trillions of bacteria primarily belonging to Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes classes, plays a crucial role in maintaining intestinal health. These diverse microbial communities aid in bolstering the immune system, breaking down dietary fibers, and facilitating nutrient absorption. They also fortify the intestinal lining, acting as a barrier against pathogens. However, disruptions in the delicate balance between the host and the gut microbiota, known as dysbiosis, may lead to various diseases, including leaky gut syndrome. In this condition, increased intestinal permeability allows toxic compounds to enter the bloodstream, triggering inflammation and other adverse effects. Comprehending the complex mechanisms of the gastrointestinal microbiome offers potential strategies for managing increased intestinal permeability and enhancing general health. Through the regulation of nutrients and immune reactions, the microbiota shows potential in averting and managing gut inflammation, underscoring its significant role in preserving gut health and bolstering overall health.
Symptoms
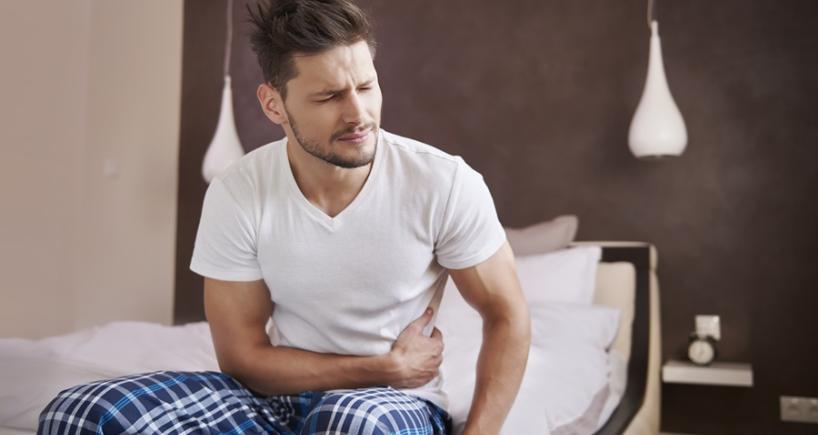
The symptoms of leaky gut syndrome exhibit a broad range and could potentially coincide with the symptoms of other medical disorders. Some of them include:
- Abdominal discomfort, such as pain, bloating, and gas
- Digestive disturbances, including diarrhea or constipation
- Fatigue
- Skin problems
- Food sensitivities
- Headaches and difficulties with concentration
Causes
While the exact etiology of leaky gut syndrome remains under investigation, several factors are thought to contribute to its development. These factors may include:
- Chronic intestinal diseases like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis
- Certain medications
- Food intolerances, such as gluten and lactose intolerances
- Stress
- Exposure to environmental toxins
Diagnosis
The assessment of a leaky gut requires a thorough examination due to the absence of a specific, universally recognized diagnostic test. The assessment techniques include:
Clinical Evaluation: Healthcare providers conduct a comprehensive review of the patient’s medical history and symptoms, including chronic diarrhea, bloating, abdominal pain, fatigue, food sensitivities, and skin issues.
Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination may be performed to assess for signs indicative of gastrointestinal dysfunction, such as tenderness in the abdomen or abnormal bowel sounds.
Blood Test: Examination of blood samples may reveal antibodies and endotoxins that suggest bacterial infiltration, providing insights into gut permeability.
Urine Test: Measurement of sugar levels in urine can indicate which sugars are passing through the intestinal walls, offering indirect evidence of increased permeability.
Tissue Biopsy: Laboratory analysis of intestinal tissue samples obtained through biopsy may reveal abnormalities indicative of altered gut permeability.
Advanced Imaging: Advanced endoscopic procedures allow for direct visualization and magnified examination of the intestinal lining, aiding in the assessment of gut permeability.
Allergy Testing: Assessment of IgE levels through allergy testing may help identify potential allergens contributing to leaky gut syndrome.
Specialized Tests: The lactulose-mannitol test involves administering a solution containing lactulose and mannitol, followed by measuring their levels in the urine to indirectly assess intestinal permeability.
Zonulin Levels Measurement: Zonulin is a protein associated with gut barrier function, and measuring its levels may provide insights into intestinal permeability.
Consultation With Specialists: Given the complexity of diagnosing leaky gut syndrome, consultation with gastroenterologists or functional medicine practitioners is recommended for proper evaluation and management.
Since the symptoms of leaky gut syndrome may overlap with those of other gastrointestinal disorders, ruling out alternative diagnoses is essential for accurate assessment and treatment planning.
Treatment Approaches
Given the lack of a recognized medical diagnosis for leaky gut syndrome, treatment approaches aim to address underlying factors contributing to intestinal permeability. Strategies may include the following methods:
Dietary Modifications:
- Eliminate trigger foods that exacerbate symptoms.
- Incorporate gut-friendly options rich in fiber, antioxidants, and essential nutrients.
Lifestyle Changes:
Regular physical activity should be undertaken to promote gastrointestinal motility and enhance overall well-being. Implementing strategies for managing stress, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises, is also recommended.
- Prioritize adequate sleep hygiene to promote gut healing and repair.
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption to reduce inflammation and support gut health.
- Minimize the unnecessary use of antibiotics to preserve gut microbiota balance.
Supplementation: Consider targeted supplements to support gut healing, such as probiotics, L-glutamine, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Consult with a healthcare professional, such as a gastroenterologist or a functional medicine practitioner, for personalized guidance and monitoring of treatment progress.
By addressing underlying factors, implementing dietary and lifestyle modifications, and potentially incorporating targeted supplementation, individuals can take proactive steps to repair and maintain gut health, alleviate symptoms associated with leaky gut syndrome, and promote overall well-being.
Conclusion
While leaky gut syndrome remains a topic of debate within the medical community, its potential implications for health cannot be dismissed outright. Individuals can be proactive in safeguarding the well-being of their gut by delving into potential triggers, identifying linked signs, investigating through various diagnostic methods, and contemplating treatment strategies. As research continues to unravel gut health’s complexities, collaboration between patients and healthcare providers remains essential in navigating this evolving landscape.
Popular Searches :
Hospitals: Cancer Hospital in Delhi | Best Heart Hospital in Delhi | Hospital in Amritsar | Hospital in Ludhiana | Hospitals in Mohali | Hospital in Faridabad | Hospitals in Gurgaon | Best Hospital in Jaipur | Hospitals in Greater Noida | Hospitals in Noida | Best Kidney Hospital in Kolkata | Best Hospital in Kolkata | Hospitals in Rajajinagar Bangalore | Hospitals in Richmond Road Bangalore | Hospitals in Nagarbhavi Bangalore | Hospital in Kalyan West | Hospitals in Mulund | Best Hospital in India | Gastroenterologist in Jaipur | Cardiology Hospital in India
Doctors: Dr. Rana Patir | Dr. Rajesh Benny | Dr. Rahul Bhargava | Dr. Jayant Arora | Dr. Anoop Misra | Dr. Manu Tiwari | Dr. Praveer Agarwal | Dr. Arup Ratan Dutta | Dr. Meenakshi Ahuja | Dr. Anoop Jhurani | Dr. Shivaji Basu | Dr. Subhash Jangid | Dr. Atul Mathur | Dr. Gurinder Bedi | Dr. Monika Wadhawan | Dr. Debasis Datta | Dr. Shrinivas Narayan | Dr. Praveen Gupta | Dr. Nitin Jha | Dr. Raghu Nagaraj | Dr. Ashok Seth | Dr. Sandeep Vaishya | Dr. Atul Mishra | Dr. Z S Meharwal | Dr. Ajay Bhalla | Dr. Atul Kumar Mittal | Dr. Arvind Kumar Khurana | Dr. Narayan Hulse | Dr. Samir Parikh | Dr. Amit Javed | Dr. Narayan Banerjee | Dr. Bimlesh Dhar Pandey | Dr. Arghya Chattopadhyay | Dr. G.R. Vijay Kumar | Dr Ashok Gupta | Dr. Gourdas Choudhuri | Dr. Sushrut Singh | Dr. N.C. Krishnamani | Dr. Atampreet Singh | Dr. Vivek Jawali | Dr. Sanjeev Gulati | Dr. Amite Pankaj Aggarwal | Dr. Ajay Kaul | Dr. Sunita Varma | Dr. Manoj Kumar Goel | Dr. R Muralidharan | Dr. Sushmita Roychowdhury | Dr. T.S. MAHANT | Dr. UDIPTA RAY | Dr. Aparna Jaswal | Dr. Ravul Jindal | Dr. Savyasachi Saxena | Dr. Ajay Kumar Kriplani | Dr. Nitesh Rohatgi | Dr. Anupam Jindal |
Specialties: Heart Lung Transplant | Orthopedic | Cardiology Interventional | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | Onco Radiation | Neurosurgery |