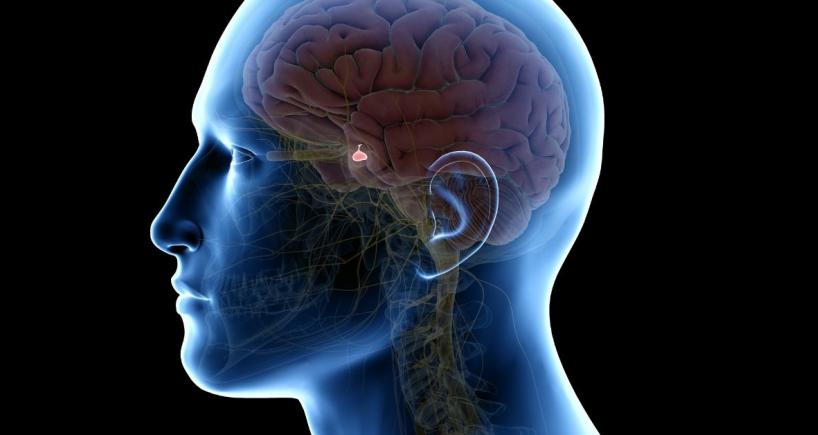
Shedding Light on Prolactinomas: Understanding Pituitary Tumors
Prolactinomas are benign tumors of the anterior pituitary which dramatically influence hormonal regulation and general health of the patient. While non-cancerous, pituitary tumors cause changes in the body’s hormonal balance and morbidity. They are connected with the production of breast milk after the birth of a child. Because of being sensitive to increased prolactin, when a prolactinoma is present, it disrupts the normal secretion and thus elicits proper symptoms related to hyperprolactinemia.
Symptoms should be reported at an early stage, a correct diagnosis, and proper management are vital in managing this disease. This is because, with the current and dynamic medical treatment and surgical procedures most of the patients with prolactinomas can have good results and live productive lives. Knowledge on prolactinomas makes the patients embrace an active role in managing their diseases and thus help them to live a healthy life.
Symptoms of Prolactinomas
Prolactinomas’ symptoms in men and women can be dramatically different because hormones are regulated differently in the two sexes.
In women, common symptoms include:
- Irregularities in milk production that occur after a woman has delivered her baby and or while breastfeeding her baby.
- Lack of, or irregular menstrual cycles.
- Infertility
- Reduced libido
- Overgrowth of hair in places where it is expected to be less or not at all.
In men, symptoms might include:
- Erectile dysfunction
- Enlargement of breast tissue.
- Decreased libido
- Infertility
- Headaches and vision problems
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of the presented case of prolactinoma is done after taking history, clinical examination, blood tests, MRI or CT scan. In the diagnosis of a patient with seriousness of prolactinoma, the patient history topped up with the physical examination is taken.
The diagnosis further includes:
• Serum prolactin assessment – This is very crucial while determining the origin of galactorrhea. Prolactin within the blood indicates that the individual is developing a prolactinoma.
• Imaging is essential with MRI as it was recommended and used to obtain clear pictures of the pituitary gland in order to assess the size as well as the location of the tumor. If situation permits, the same is done through a computed tomography (CT scan).
Treatment Options for Prolactinomas
Thus, the management of prolactinomas is mainly determined by the size of the tumor, the intensity of clinical symptoms expressed, and the state of the patient’s health and his/her wishes. There are three primary treatment options: such as, drugs, operations, and radiation.
• Medication: It inhibits dopamine which is responsible for inhibition of prolactin secretion and contributes to regulation of the size of the tumour and reduction of the patients’ symptoms at the same time. These drugs are not contraindicative with most of the affected patients and hence such patients do not need to undergo surgery or radiation.
• Surgery: It is a surgery in which tumor is removed through nostrils without the necessity to open up the skull. When used when there is failure in treatment or if tumor is large to handle the side effects of the drugs or the patient cannot endure the drugs. Thus, cure rate after the surgery is still high especially if the tumor size is relatively small but maladies that are emergent with the surgery are that the surrounding tissues become infected or the patient may end up with hormonal problems.
• Radiation Therapy: This intervention is usually applied when medication and surgery interventions are not useful or can not be implemented. Radiation therapy utilizes beams of radiation on the affected area in an attempt to kill the tumor cells. It can be applied through traditional external beam radiation or other more accurate methods such as stereotactic radiosurgeries. The effects of radiation therapy are cumulative and the improvement of the symptoms may be observed in weeks, months or even years.
Living with Prolactinomas
Although prolactinoma is a serious condition, it is not the end of the world because like other illnesses, patients with this condition can equally live healthy lives if diagnosed early and managed well. Subsequent visits in an endocrinologist should be scheduled in order to maintain the balance of prolactin and to exclude the presence of a tumor again. Patients should also note and report any alteration in the original signs or the emergence of other signs and symptoms regarding their illness.
Perhaps, the most instructive are changes in daily habits as they can enhance the effectiveness of primary pharmacological therapy and positively impact the patient’s quality of life. Practical aspects in the lifestyle, such as reliable nutrition and regular exercise and stress reduction, play an important role in hormonal regulation and the body’s ability to overcome health issues.
Support groups can be helpful to the patient in handling prolactinomas since it has considerable effect on the psychological welfare of the patient. Often it is helpful to find people with similar profiles, to know that they are not alone and that they can work towards lifting themselves up.