Signs and Treatments of Chagas Disease
Introduction
Chagas disease, commonly referred to as American trypanosomiasis, is a tropical parasitic illness caused by the protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi. It has generally affected the rural population of Latin America, but with growing reports all over the world, this disease has become a cause for alarm because, if left untreated, it can be fatal. The treatment will usually make interventions before it reaches critical stages, such as very severe heart and digestive problems.
What is Chagas disease?
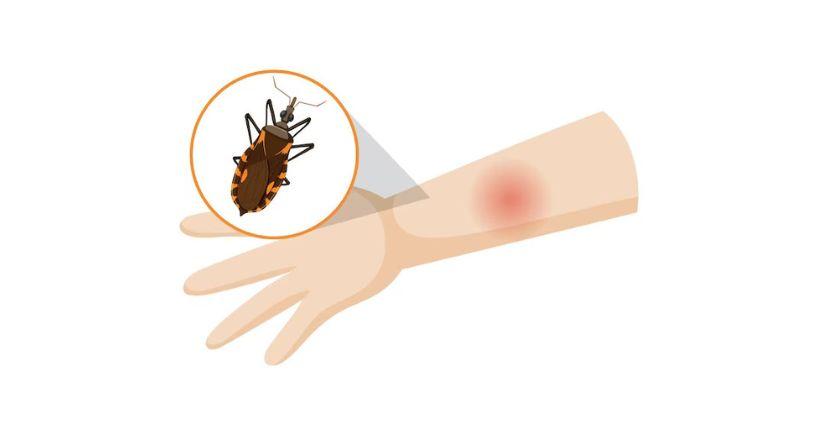
This disease is caused by being bitten by an infected insect called the triatomine bug; in English, this is commonly referred to as the ‘kissing bug’. It can enter this illness through the site of the wound made by its bite or even directly through mucous membranes, like in the eyes or mouth, via the parasite called Trypanosoma cruzi. It is passed on also through contaminated food, blood transfusions, organ transplants, and even from mother to child during pregnancy.
Chagas disease contains two stages: Acute and chronic. The acute stage occurs directly after the infection, while the chronic stage may take years to fully develop; in most cases, it may become fatal if left untreated.
Chagas disease symptoms
Symptoms of the acute phase:
- Fever
- Malaise
- Swelling of the area where the infection occurs
- Skin rash
- Headache
- Body aches
- Lymph nodes
Even though acute phase symptoms may resolve spontaneously, the infection in the body continues and progresses into the chronic phase, where more severe health complications seem to develop.
Symptoms of the chronic phase:
In the chronic phase, where the parasite silently causes irreversible damage to critical organs, namely heart and digestive system functions, it may last for decades. It is estimated that about 30% of infected people will eventually develop severe health complications.
- Cardiac symptoms: Arrhythmias, palpitations, heart failure, and even sudden death in extreme cases. Chagas disease is considered one of the leading causes of heart problems in endemic regions.
- Digestive symptoms: Enlargement of such organs as the oesophagus or the colon leads to problems in swallowing, persistent constipation, and pain in the abdominal cavity.
- Damage to nerves: Neurological complications are not common; they involve decreased motor skills and so on.
- Congestive heart failure: Untreated Chagas disease can eventually cause an enlarged heart. The heart eventually becomes inefficient in pumping blood.
Diagnostic techniques
- Blood tests: These helps diagnose the presence of Trypanosoma cruzi at the acute phase, which is often identified through microscopy or PCR.
- Serological tests: These tests identify antibodies to the parasite. Thus, they are quite frequently used in diagnosing chronic infections.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): In the chronic phase, ECGs are quite commonly used to monitor abnormal heart conditions in patients displaying cardiac symptoms.
- Imaging tests: Patients suffering from the disorder may need X-rays or endoscopy to determine the level of damage in organs like the oesophagus and colon.
Treatment
Early detection is essential for management. The only way to help treat the symptoms and the general progression of the disease is with the application of antiparasitic medicines.
Antiparasitic drugs: These drugs have always been known to be most effective when acting on the patient within the acute phase, and there is a chance that they can even take the parasite out of the host’s body.
Syndromic therapy: The management of Chagas disease in the chronic phase comprises relief from symptoms and complications. It includes:
- Heart medications: For patients who have conduction abnormalities, treatment may encompass beta-blockers and other drugs that decrease arrhythmias and heart failure.
- Gastrointestinal management: Patients with gastrointestinal problems might require surgery to remove constrictions in the oesophagus or intestines.
Prevention and control
Chagas disease prevention focuses on the control of vectors in endemic regions and housing improvement measures. Main strategies include:
- Vector control: Pesticides, distribution of nets, and sealing crevices and cracks of houses remove the entry points of the triatomine bug.
- Blood screening: Screening blood donors in the endemic area’s limits transmission through blood transfusion.
- Health education: Educating communities about the dangers of Chagas disease and educating them on personal protective measures, such as bed net use, is deemed a key step in reducing rates of infection.
Conclusion
Chagas disease is a serious tropical illness that can silently progress to severe cardiac and digestive complications. Ensuing early symptoms, timely diagnosis, and appropriate treatment can improve outcomes for the infected. Even though the use of antiparasitic drugs offers the best hope for early recovery, it is crucial to manage long-term complications for patients in the chronic phase. Preventive efforts remain paramount in dealing with the widespread expansion of this non-acknowledged disease, particularly in endemic regions. This leads to overcoming the challenges responsible for raising awareness for signs, treatments, and preventive strategies among the affected populations across the globe to minimise the impact of Chagas disease.
Popular Searches :
Hospitals: Cancer Hospital in Delhi | Best Heart Hospital in Delhi | Hospital in Amritsar | Hospital in Ludhiana | Hospitals in Mohali | Hospital in Faridabad | Hospitals in Gurgaon | Best Hospital in Jaipur | Hospitals in Greater Noida | Hospitals in Noida | Best Kidney Hospital in Kolkata | Best Hospital in Kolkata | Hospitals in Rajajinagar Bangalore | Hospitals in Richmond Road Bangalore | Hospitals in Nagarbhavi Bangalore | Hospital in Kalyan West | Hospitals in Mulund | Best Hospital in India | | Cardiology Hospital in India | Best Cancer Hospital in India | Best Cardiology Hospital in India | Best Oncology Hospital In India | Best Cancer Hospital in Delhi | Best Liver Transplant Hospital in India
Doctors: Dr. Rana Patir | Dr. Rajesh Benny | Dr. Rahul Bhargava | Dr. Jayant Arora | Dr. Anoop Misra | Dr. Manu Tiwari | Dr. Praveer Agarwal | Dr. Arup Ratan Dutta | Dr. Meenakshi Ahuja | Dr. Anoop Jhurani | Dr. Shivaji Basu | Dr. Subhash Jangid | Dr. Atul Mathur | Dr. Gurinder Bedi | Dr. Monika Wadhawan | Dr. Debasis Datta | Dr. Shrinivas Narayan | Dr. Praveen Gupta | Dr. Nitin Jha | Dr. Raghu Nagaraj | Dr. Ashok Seth | Dr. Sandeep Vaishya | Dr. Atul Mishra | Dr. Z S Meharwal | Dr. Ajay Bhalla | Dr. Atul Kumar Mittal | Dr. Arvind Kumar Khurana | Dr. Narayan Hulse | Dr. Samir Parikh | Dr. Amit Javed | Dr. Narayan Banerjee | Dr. Bimlesh Dhar Pandey | Dr. Arghya Chattopadhyay | Dr. G.R. Vijay Kumar | Dr Ashok Gupta | Dr. Gourdas Choudhuri | Dr. Sushrut Singh | Dr. N.C. Krishnamani | Dr. Atampreet Singh | Dr. Vivek Jawali | Dr. Sanjeev Gulati | Dr. Amite Pankaj Aggarwal | Dr. Ajay Kaul | Dr. Sunita Varma | Dr. Manoj Kumar Goel | Dr. R Muralidharan | Dr. Sushmita Roychowdhury | Dr. T.S. MAHANT | Dr. UDIPTA RAY | Dr. Aparna Jaswal | Dr. Ravul Jindal | Dr. Savyasachi Saxena | Dr. Ajay Kumar Kriplani | Dr. Nitesh Rohatgi | Dr. Anupam Jindal
Specialties: Heart Lung Transplant | Orthopedic | Cardiology Interventional | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | Onco Radiation | Neurosurgery | Interventional Cardiology | Gastroenterologist in Jaipur | Neuro Physician | Gynecologist in Kolkata | Best Neurologist in India | Liver Transfer | Best Cardiologist in Delhi