Understanding Pulmonary Edema: Causes and Treatments
What leads to Pulmonary Edema?
You can consider your lung like a sponge that absorbs oxygen and releases carbon dioxide during respiration to allow for gaseous exchange. This sponge becomes saturated with water when one is affected by pulmonary edema. Instead of allowing oxygen into your bloodstream like they should, alveoli get filled with fluids, thereby impeding oxygen transfer, that results into dangerous deficiency of oxygen inside our bodies.
Causes of Pulmonary Edema:
Several reasons can cause pulmonary edema, but it primarily falls under two categories.
Cardiac Pulmonary Edema is the most common type brought by issues with heart function. It usually develops when the left ventricle of the human heart, mainly responsible for pumping oxygenated blood to different parts of the body becomes feeble such that it fails to drive the same amount of blood forward. Consequently, pressure builds up within these blood vessels in the lungs leading to seepage of fluids into their air-filled sacs.
Cardiogenic causes pulmonary edema include:
Heart disease-This is a continuous sickness that causes the heart to stop pumping properly.
Coronary Artery Disease-It is an illness consisting of blocking off blood passages or narrowing them so that they don’t allow enough blood into the heart muscle
High Blood Pressure- Put more strain on the arteries but can lead to heart failure
Valvular Heart Disease-The heart valves do not let blood flow properly through them
Non-Cardiac Pulmonary Edema: When water collects in the lungs due to reasons other than those linked to the heart functioning.
The following are the commonly occurring causes of non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema:
Acute respiratory distress syndrome, ARDS: Major injury to the lungs usually caused by infection, sepsis, trauma, or aspiration.
High altitude pulmonary edema: Fluid accumulation at high altitudes with reduced oxygen pressure.
Overdosing on drugs: Certain drugs, like narcotics, that depress respiration may lead to fluid accumulation.
Kidney failure: Impairment in the kidney function can lead to water retention, and that could involve the lungs.
Infection: Pneumonia or any other infectious disease of the lungs can cause inflammation and fluid collection.
Symptoms of Pulmonary Edema:
The symptoms have to be identified at an early stage so that immediate medical attention can be sought. Some common signs are:
Shortness of breath: Especially upon exertion or when lying down.
Wheezing: A whistling sound when breathing.
Coughing: Mostly, frothy sputum that is pink-tinged.
Rapid heartbeat: The heart tries to compensate for the reduced oxygen levels.
Fatigue: Weak and exhausted due to oxygen deficiency.
Anxiety and restlessness: Mostly accompany the discomfort of breathing difficulty.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Edema:
You will be examined by a healthcare professional, listen to your lungs, and assess your general health. They may order tests like:
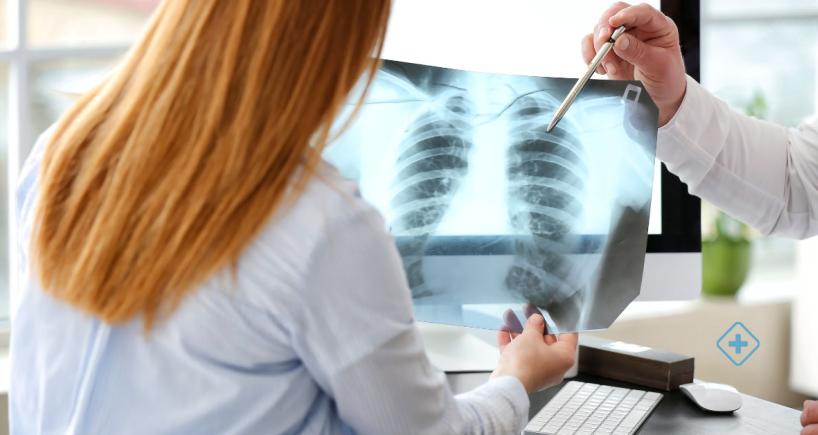
Chest X-ray: Visualize fluid buildup in the lungs.
Electrocardiogram (ECG): Verify your heart’s electrical activity.
Blood tests: Evaluate blood oxygen levels and kidney function. Echocardiogram: Assess the structure and function of your heart.
Treatment depends on what has caused the problem and how serious it is. Treatment options for Pulmonary Edema:
Oxygen therapy: This is where more oxygen is provided so that there is enough available oxygen in the body for use by tissues.
Drugs: Diuretics which help take out extra water from the body. Vasodilators that help to relax blood vessels and increase blood flow. Inotropes which make the heart pump better.
Mechanical ventilation which helps in severe cases for a person to breathe well. Intubation where a tube is put through the mouth or nose into the throat to help breath.
Preventing Pulmonary Edema:
Although not all cases of pulmonary edema are preventable, there are ways in which you can lower your risk.
Manage heart conditions: Control blood pressure, keep cholesterol levels healthy, and manage heart disease.
Quit smoking: When people smoke, it damages the lungs, which in turn increases the chance that they will develop pulmonary edema.
Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity causes extra stress on the heart.
Regular exercise: Better for your heart’s structure and improves its overall health
Follow doctor's advice: Always follow medication instructions as well as going for treatment as soon as you notice anything wrong.
Pulmonary edema is a serious condition, but timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment can significantly improve outcomes. By understanding why it happens, signs you should watch out for, and treatment methods associated with it, you can be able to seek timely medical help to ensure optimum lung functioning.
Popular Searches :
Hospitals: Cancer Hospital in Delhi | Best Heart Hospital in Delhi | Hospital in Amritsar | Hospital in Ludhiana | Hospitals in Mohali | Hospital in Faridabad | Hospitals in Gurgaon | Best Hospital in Jaipur | Hospitals in Greater Noida | Hospitals in Noida | Best Kidney Hospital in Kolkata | Best Hospital in Kolkata | Hospitals in Rajajinagar Bangalore | Hospitals in Richmond Road Bangalore | Hospitals in Nagarbhavi Bangalore | Hospital in Kalyan West | Hospitals in Mulund | Best Hospital in India | | Cardiology Hospital in India | Best Cancer Hospital in India | Best Cardiology Hospital in India | Best Oncology Hospital In India | Best Cancer Hospital in Delhi | Best Liver Transplant Hospital in India
Doctors: Dr. Rana Patir | Dr. Rajesh Benny | Dr. Rahul Bhargava | Dr. Jayant Arora | Dr. Anoop Misra | Dr. Manu Tiwari | Dr. Praveer Agarwal | Dr. Arup Ratan Dutta | Dr. Meenakshi Ahuja | Dr. Anoop Jhurani | Dr. Shivaji Basu | Dr. Subhash Jangid | Dr. Atul Mathur | Dr. Gurinder Bedi | Dr. Monika Wadhawan | Dr. Debasis Datta | Dr. Shrinivas Narayan | Dr. Praveen Gupta | Dr. Nitin Jha | Dr. Raghu Nagaraj | Dr. Ashok Seth | Dr. Sandeep Vaishya | Dr. Atul Mishra | Dr. Z S Meharwal | Dr. Ajay Bhalla | Dr. Atul Kumar Mittal | Dr. Arvind Kumar Khurana | Dr. Narayan Hulse | Dr. Samir Parikh | Dr. Amit Javed | Dr. Narayan Banerjee | Dr. Bimlesh Dhar Pandey | Dr. Arghya Chattopadhyay | Dr. G.R. Vijay Kumar | Dr Ashok Gupta | Dr. Gourdas Choudhuri | Dr. Sushrut Singh | Dr. N.C. Krishnamani | Dr. Atampreet Singh | Dr. Vivek Jawali | Dr. Sanjeev Gulati | Dr. Amite Pankaj Aggarwal | Dr. Ajay Kaul | Dr. Sunita Varma | Dr. Manoj Kumar Goel | Dr. R Muralidharan | Dr. Sushmita Roychowdhury | Dr. T.S. MAHANT | Dr. UDIPTA RAY | Dr. Aparna Jaswal | Dr. Ravul Jindal | Dr. Savyasachi Saxena | Dr. Ajay Kumar Kriplani | Dr. Nitesh Rohatgi | Dr. Anupam Jindal |
Specialties: Heart Lung Transplant | Orthopedic | Cardiology Interventional | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | Onco Radiation | Neurosurgery | Interventional Cardiology | Gastroenterologist in Jaipur | Neuro Physician | Gynecologist in Kolkata | Best Neurologist in India | Liver Transfer