What is Appendicitis: Understanding Types and Treatment Options
All About Appendicitis
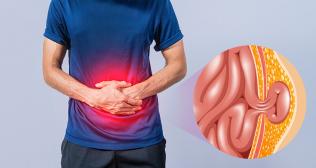
Appendicitis refers to a condition in which the appendix gets inflamed. The appendix is a small pouch attached to the end of the large bowel (intestine).
Different Types of Appendicitis
- Acute Appendicitis: Occurs suddenly, with more serious symptoms that can worsen rapidly. This condition is regarded as a medical emergency that needs immediate treatment from a healthcare professional.
- Chronic Appendicitis: Occurs when inflammation of the appendix persists over a long period, causing manifestations that come and go. This type of appendicitis is rare, accounting for only 1–5% of all appendicitis cases.
Reason of Appendicitis
- It occurs when the inside of the appendix is blocked.
- It may be caused by a variety of infectious agents, like virus, bacteria, or parasites, in the gastrointestinal tract.
- It may occur when the tube that connects the large intestine and the appendix is blocked or trapped by stool.
- Sometimes, tumors can trigger appendicitis.
Common Symptoms Of Appendicitis
- Appendicitis usually begins with a pain in the middle of the stomach that may come and go.
- Eventually, in a few hours, the pain generally moves closer to the appendix and becomes critical and constant.
- Pressing on this portion, coughing, or walking might worsen the pain.
- The affected individual might lose appetite, feel sick, and experience constipation or diarrhea.
Diagnosis of Appendicitis
Healthcare professionals will ask about health history and perform a physical exam. They also prescribe some tests, including:
- Blood Tests: To check for signs of infection, like having a high white blood cell count
- Urine Tests: To detect urinary tract infection
They may also ask the affected individual to undergo some imaging tests, including:
- Abdominal Ultrasound: Lets the doctor observe internal organs as they work and assess how the blood is flowing through distinct blood vessels
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: CT Scan shows detailed pictures of any body part, like the bones, muscles, fat, and organs
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI sometimes used to diagnose appendicitis, especially in a pregnant woman
Treatment Option Available for Appendicitis
The standard treatment of appendicitis comprises both medicines and surgery, though in a few cases, medicines might be enough.
Almost everyone will require antibiotics for appendicitis. Even if an individual doesn’t have an infection to start with, appendicitis generally leads to one.
In its early stages, when appendicitis is very mild, the healthcare professionals might follow a wait-and-watch strategy. In this approach, they observe if antibiotics alone can improve the condition of the affected individual. Individuals might prefer this approach if they have risk factors that make surgery less safe. However, healthcare professionals do not generally advise this approach as appendicitis can revert until the appendix is removed.
Individuals may also require medicine for relieving pain that they can receive through an IV. If an individual is having surgery, they’ll receive general anesthesia so they won’t be conscious (awake) during the procedure.
The appendix may be removed in an open procedure or through laparoscopy.
- Open (Traditional) Surgery Method: The individual is given anesthesia. A cut is made in the lower right-hand side of the stomach. The surgeon locates the appendix and takes it out. If the appendix bursts, a tiny tube may be inserted to drain out pus and other fluids in the belly. The shunt will be removed in a few days, when surgeon feels the infection has warded off.
- Laparoscopic Method: The individual is given anesthesia. This surgery uses several small cuts and a camera to glance inside the stomach. The surgical tools are inserted through a few minor cuts. The laparoscope is inserted through another incision. A laparoscopy can often be performed even if the appendix has burst.
If the appendix has not burst, then recovery from an appendectomy will only take a few days. If the appendix has burst, the recovery duration will be longer, and the individual will need an antibiotic.
Individuals can live a normal life without an appendix. Modifications in diet or physical activity are generally not required.
If an individual experiences the manifestations of appendicitis, they should consult a healthcare professional right away to avoid complications, which can be dreadful.
Popular Searches :
Hospitals: Cancer Hospital in Delhi | Best Heart Hospital in Delhi | Hospital in Amritsar | Hospital in Ludhiana | Hospitals in Mohali | Hospital in Faridabad | Hospitals in Gurgaon | Best Hospital in Jaipur | Hospitals in Greater Noida | Hospitals in Noida | Best Kidney Hospital in Kolkata | Best Hospital in Kolkata | Hospitals in Rajajinagar Bangalore | Hospitals in Richmond Road Bangalore | Hospitals in Nagarbhavi Bangalore | Hospital in Kalyan West | Hospitals in Mulund | Best Hospital in India | | Cardiology Hospital in India | Best Cancer Hospital in India | Best Cardiology Hospital in India | Best Oncology Hospital In India | Best Cancer Hospital in Delhi | Best Liver Transplant Hospital in India
Doctors: Dr. Rana Patir | Dr. Rajesh Benny | Dr. Rahul Bhargava | Dr. Jayant Arora | Dr. Anoop Misra | Dr. Manu Tiwari | Dr. Praveer Agarwal | Dr. Arup Ratan Dutta | Dr. Meenakshi Ahuja | Dr. Anoop Jhurani | Dr. Shivaji Basu | Dr. Subhash Jangid | Dr. Atul Mathur | Dr. Gurinder Bedi | Dr. Monika Wadhawan | Dr. Debasis Datta | Dr. Shrinivas Narayan | Dr. Praveen Gupta | Dr. Nitin Jha | Dr. Raghu Nagaraj | Dr. Ashok Seth | Dr. Sandeep Vaishya | Dr. Atul Mishra | Dr. Z S Meharwal | Dr. Ajay Bhalla | Dr. Atul Kumar Mittal | Dr. Arvind Kumar Khurana | Dr. Narayan Hulse | Dr. Samir Parikh | Dr. Amit Javed | Dr. Narayan Banerjee | Dr. Bimlesh Dhar Pandey | Dr. Arghya Chattopadhyay | Dr. G.R. Vijay Kumar | Dr Ashok Gupta | Dr. Gourdas Choudhuri | Dr. Sushrut Singh | Dr. N.C. Krishnamani | Dr. Atampreet Singh | Dr. Vivek Jawali | Dr. Sanjeev Gulati | Dr. Amite Pankaj Aggarwal | Dr. Ajay Kaul | Dr. Sunita Varma | Dr. Manoj Kumar Goel | Dr. R Muralidharan | Dr. Sushmita Roychowdhury | Dr. T.S. MAHANT | Dr. UDIPTA RAY | Dr. Aparna Jaswal | Dr. Ravul Jindal | Dr. Savyasachi Saxena | Dr. Ajay Kumar Kriplani | Dr. Nitesh Rohatgi | Dr. Anupam Jindal |
Specialties: Heart Lung Transplant | Orthopedic | Cardiology Interventional | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | Onco Radiation | Neurosurgery | Interventional Cardiology | Gastroenterologist in Jaipur | Neuro Physician | Gynecologist in Kolkata | Best Neurologist in India | Liver Transfer |