Understanding Varicose Veins: Causes, Symptoms, Risk Factors & Treatment Options
Varicose veins are a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Despite their prevalence, many individuals may not fully understand the causes, symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options associated with varicose veins. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of varicose veins, providing valuable insights to help you better understand and manage this condition.
What are Varicose Veins?
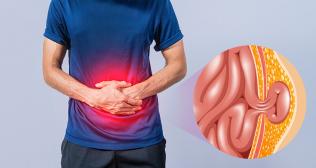
Varicose veins are enlarged, twisted, and bulging veins that commonly appear on the legs and feet. They occur when the valves within the veins fail to function properly, causing blood to pool and accumulate within the veins. This results in increased pressure, leading to the characteristic appearance of varicose veins.
Causes of Varicose Veins:
Faulty Valves: The primary cause of varicose veins is malfunctioning valves within the veins. Healthy veins contain one-way valves that prevent blood from flowing backward. When these valves weaken or become damaged, blood can flow backward and pool in the veins, leading to varicose veins.
Weak Vein Walls: Weakness in the walls of the veins can contribute to the development of varicose veins. Over time, the walls of the veins may lose their elasticity and become stretched, allowing the veins to bulge and become visible beneath the skin.
Heredity: Genetic factors play a significant role in the development of varicose veins. Individuals with a family history of varicose veins are more likely to develop the condition themselves.
Pregnancy: Pregnancy can increase the risk of varicose veins due to hormonal changes, increased blood volume, and pressure on the veins from the growing uterus. Varicose veins that develop during pregnancy often improve or resolve after childbirth. Obesity: Excess weight can place additional pressure on the veins, increasing the risk of varicose veins.
Symptoms of Varicose Veins:
Varicose veins may cause a range of symptoms, including:
- Visible veins: Bulging, twisted veins that are visible beneath the skin, typically on the legs and feet.
- Pain or discomfort: Aching, throbbing, or heaviness in the legs, especially after prolonged standing or sitting.
- Swelling: Swelling, particularly in the ankles and feet, due to fluid accumulation.
- Itching or burning: Irritation or discomfort around the affected veins.
- Skin changes: Discoloration, redness, or inflammation near the varicose veins.
- Complications: In severe cases, varicose veins may lead to complications such as skin ulcers or blood clots.
Risk Factors for Varicose Veins:
Several factors increase the risk of developing varicose veins, including:
- Age: The risk of varicose veins increases with age, as the veins naturally lose elasticity over time.
- Gender: Women are more likely than men to develop varicose veins, possibly due to hormonal fluctuations and pregnancy.
- Family History: A family history of varicose veins increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and increased pressure on the veins during pregnancy can contribute to varicose veins.
Obesity: Excess weight places additional strain on the veins, increasing the risk of varicose veins.
Treatment Options for Varicose Veins:
Lifestyle Modifications: Making lifestyle changes can help alleviate symptoms and reduce the risk of varicose veins worsening. Recommendations may include regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, elevating the legs when resting, avoiding prolonged periods of sitting or standing, and wearing compression stockings.
Minimally Invasive Procedures: Several minimally invasive procedures are available to treat varicose veins, including:
Sclerotherapy: This procedure involves injecting a solution into the affected veins, causing them to collapse and fade over time.
Endovenous Laser Ablation (EVLA): EVLA uses laser energy to seal off the affected veins, redirecting blood flow to healthier veins.
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): RFA uses heat energy to close off varicose veins, promoting their collapse and eventual disappearance.
Surgical Intervention: In severe cases or when other treatments have been ineffective, surgical procedures such as vein stripping or ligation may be recommended to remove or tie off the affected veins.
Conclusion:
Varicose veins are a common and often bothersome condition that can impact an individual's quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options associated with varicose veins, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition effectively. If you are experiencing symptoms of varicose veins or have concerns about your vein health, consult with a qualified healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. With the right approach, varicose veins can be effectively treated, improving both physical comfort and overall well-being.
Categories
Clear allMeet the doctor

- General Surgery | General Surgery
-
20 Years
-
1100