Collagen Deficiency Signs, Causes and How to Treat It
Collagen is a basic constituent of hair, connective tissues and the skin. It is an essential structural protein supporting skin tone, elasticity, joint strength, and well-being. However, the body produces collagen, and the production reduces with age, causing several symptoms that indicate the deficiency.
Signs of collagen deficiency
Lack of collagen mainly exhibits itself as changes in the skin and joints, but the effects are found deeper than that. Here are some common signs:
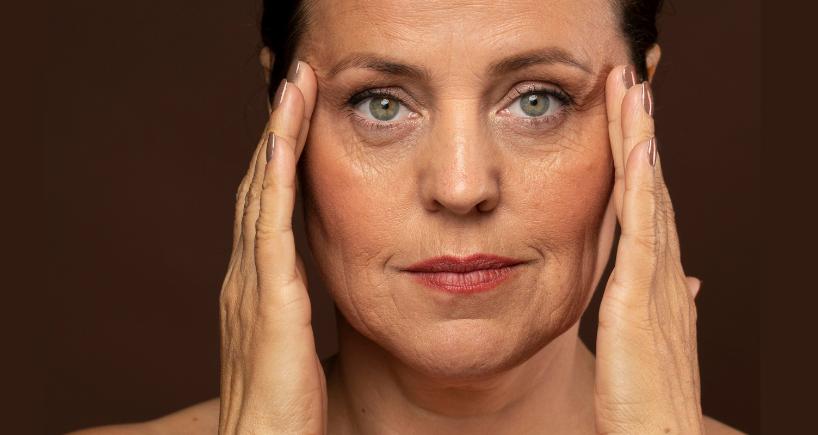
- Skin ageing and wrinkles: Lack of production of collagen makes the skin lose its elasticity, thus resulting in wrinkles, lines and sagging skin. The skin may appear opaque or leather-like and seems to be contributing to the ageing process.
- Joint pain and stiffness: One can say that collagen is a structural protein of cartilage. A deficiency may cause joint aches, tightness or even osteoarthritis, where the cartilage wears out.
- Weakened hair and nails: They concluded that collagen promotes hair and nails strength and growth. Lack of it can cause the nails to become brittle and hair to start thinning.
- Delayed wound healing: Collagen is an important aspect of the healing processes of the tissue. Its deficiency can cause delays in the rate by which cuts and injuries heal.
- Loss of muscle mass: More significantly, collagen plays a role in maintaining muscle structure, and consequently, it can result in more frail muscles and reduced muscle size over time.
What causes collagen deficiency?
Several factors contribute to collagen depletion, some of which are natural, while others are lifestyle-driven:
- Ageing: Hyaluronic acid synthesis is steadily reduced from the age of 20, and annually, its synthesis rate is cut by 1%. This natural decline is more enhanced during the menopausal period in women.
- Unhealthy diet: Vitamin C, zinc and particular amino acids, which are needed by the body to produce collagen as they could be scarce in such diets and, therefore, impede collagen synthesis.
- Ultraviolet (UV) rays cause the breakdown of collagen fibres, resulting in early skin ageing and wrinkle formation.
- Smoking and alcohol: Tobacco smoke lets the skin elasticity diminish, while excessive drinking erodes the collagen – causing facial volume and skin firmness.
- Chronic stress: Stress causes cortisol – a particularly destructive hormone that breaks tissue and collagen, which is required for the skin.
Addressing collagen deficiency
Treating collagen deficiency involves both dietary and lifestyle adjustments, along with targeted supplementation:
- Dietary changes: Incorporate collagen-rich or collagen-boosting foods into your diet. They include:
- Bone broth: An extract source of collagen peptides
- Citrus fruits: Rich in vitamin C, which plays a role in collagen production
- Leafy greens: Have antioxidants that protect the present collagen in the body
- Fish and eggs: Offer amino acids necessary for creating the effective foundation for collagen
- Supplements: In general, the decision on the right collagen supplements for women to take to treat deficiencies adequately lies in achieving this. It is recommended to use hydrolysed collagen peptides, which the body absorbs quickly and without problems. Marine collagen is very useful for skin health because of its high biological availability.
- Topical treatments: Skin care creams that include retinoid, hyaluronic acid, peptides and some natural ingredients are useful in encouraging collagen formation and increasing skin firmness.
- Protect your skin: Skin ageing can also occur due to UV damage of collagen. Therefore, use sunscreen every day. Other precautions that cannot be overlooked include wearing protective clothing and avoiding the sun.
Lifestyle adjustments
- Smoking also damages your collagen, so it’s time to kick this habit.
- Because alcohol also breaks down collagen, it is advisable to consume it at moderate levels.
- Yoga, meditation or exercises help reduce cortisol rates; hence, they help manage stress.
Collagen and women’s health
Collagen declines in everyone as they age, but women have a steeper drop, especially after menopause. These effects can be fought off by supplementing with collagen; the skin’s tone and flexibility would be enhanced, and joint pains eliminated. The ideal collagen for women comes with bonus nutrients such as biotin and vitamin C to increase the bioavailability of collagen.
Conclusion
While collagen deficiency is indeed a natural part of the ageing process, there’s still hope for reversing the process. Therefore, when you identify signs such as skin ageing, joint pains and brittle nails, you can reverse the process and build collagen. A balanced diet, the right supplements and good lifestyle changes go a long way towards keeping your collagen steady and healthy. By purchasing the best qualities of collagen and ensuring that your skin is protected, you will likely be rewarded with young, beautiful skin and strong joints.