What Are Insulin Shots? Understanding Their Definition, Functions and Types
You may be familiar with the condition called diabetes. It leads to an abnormal increase in the blood sugar levels of the body. The glucose level in the bloodstream is regulated by the insulin. When the pancreas doesn’t secret enough insulin, glucose levels build up in the bloodstream, causing diabetes. It is often known as diabetes mellitus. The pancreas naturally produces the hormone called insulin, which is necessary for the body to be able to use sugar or glucose. Hyperglycaemia is the result of either insufficient insulin production by the pancreas or improper insulin usage by the body. In order to control diabetics, a person either the condition utilises artificial forms of insulin.
Insulin
Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas. Your body uses glucose as its primary and preferred energy source. Both the food and beverages you consume and the naturally released glucose stored in your body are the sources of glucose.
Functions of insulin
The body cells in humans require energy. Glucose can leave your circulation and enter the cells, where it can be used as fuel once insulin unlocks the cell doors. Insufficient insulin prevents glucose from entering the cells, causing it to accumulate in the blood. Diabetes and elevated blood sugar are the results of insufficient insulin in the body. Diabetes-related ketoacidosis, a potentially fatal consequence, is brought on by a complete lack of insulin for an extended period of time.
Insulin moves glucose from the blood into muscles and other tissues for energy. Pancreatic alpha cells release the hormone glucagon when the blood sugar falls. Pancreatic beta cells in the islets of Langerhans release insulin when blood sugar levels rise.
Conditions that require insulin as a treatment
Diabetes: Glucose in the bloodstream is regulated by the insulin. When the pancreas doesn’t secret enough insulin, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, causing diabetes.
- Type 1 diabetes: It is a condition where your immune system damages its insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. It is a rare condition of diabetes.
- Type 2 diabetes: It is a type where the pancreas secretes less amount of insulin, and the body doesn’t respond normally to the insulin. It is the most common diabetes seen in adults and elders.
- Type 3 diabetes: It is a condition that occurs when the pancreas is damaged, which results in the insufficient production of insulin. It is caused by other conditions, like pancreatic cancer, cystic fibrosis, hemochromatosis, etc.
Prediabetes: It is an autoimmune condition, which is a stage that occurs before type 2 diabetes.
Gestational diabetes: It is a condition that occurs only during pregnancy. It fades away after pregnancy. If not, there will be a chance of getting type 2 diabetes.
Latent autoimmune diabetes in adults: This condition is caused by an autoimmune disorder, such as type 1 diabetes. It is caused in people above 30 years.
Maturity onset diabetes in young (MODY): It is caused by an inherited genetic mutation that affects insulin production in the body. It is often known as monogenic diabetes.
Neonatal diabetes: It is a rare condition that occurs in babies in the first six months. It is a form of monogenic diabetes. Gradually, it is cured, but in some cases, it may reappear, and the condition is called transient neonatal diabetes mellitus.
Brittle diabetes: It is a kind of type 1 diabetes that leads to serious conditions.
Types of insulin
Insulin comes in a variety of forms. In the event that you have diabetes, an appropriate kind or type of insulin is given. According to the duration, the rate of action insulin can be classified as follows:
- Rapid-acting insulin: It is a kind which gives effect within five to twenty minutes of administration and lasts for five hours. It is most effective about an hour after infection. It is given before the meals.
- Intermediate-acting insulin: This type of insulin lasts for about twelve hours after injection.
- Long-lasting insulin: It lasts for about fourteen hours and regulates the glucose level in the blood.
- Ultra-long-lasting insulin: This kind of insulin reaches the bloodstream in six hours and lasts for two to three days after injection.
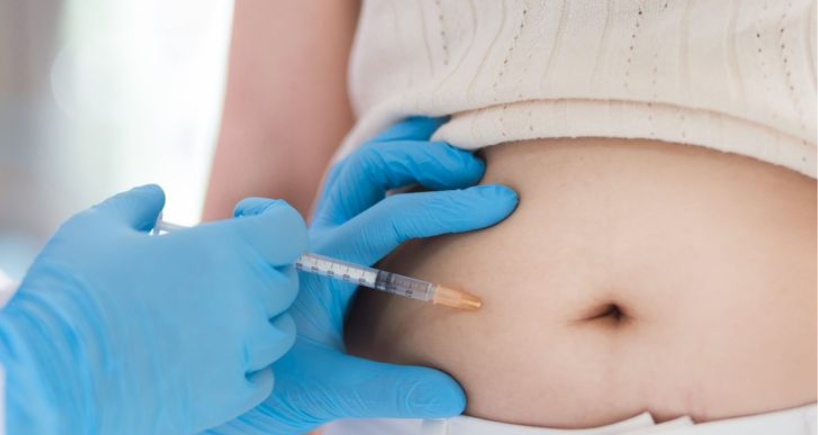
Sites of injection for insulin
Insulin can be injected in several areas of the body where the body fats, that is, adipose tissues, are present. They are:
- Belly region
- Front or side of thighs
- Back of upper arms
- Upper buttocks
Conclusion
To conclude, insulin regulates the blood glucose levels. When insulin is produced less, it leads to a condition known as diabetes. Hence, insulin is supplied externally through injections as a treatment to cure diabetes. There are many types of insulin given based on the type of diabetes.