What is Acne : Uncover The Causes and Effective Treatment Choices
Introduction
Sebum prevents skin dryness. However, along with dead skin cells, sebum clogs the pores, forming lesions commonly known as pimples (acne). Everyone has experienced a pimple breakout at least once in their lifetime. Most often, the outbreaks occur on the face but can also manifest on the upper back, chest, neck, and shoulders. Many TV commercials nowadays try to boost the affected individuals’ confidence by displaying the transformation people have undergone in their fight against skin conditions. Acne in most individuals usually fade off by the age of thirties. However, in some individuals, acne persist even in their forties and fifties.
Unveiling the Causes of Acne
It is believed that one or more of the following factors can lead to the development of acne:
- Too much (excess) production of oil in the pores
- Aggregation of dead skin cells in the pore
- Proliferation of bacteria in the pores
The following factors might increase the chances of getting acne:
- Family History: Studies show that an individual might be more likely to get acne if their parents had acne.
- Hormones: An increase in androgens (male sex hormones) might lead to acne. These increase in both boys and girls, usually during adolescence, and cause the sebaceous glands to enlarge and produce more sebum. Hormonal modifications related to pregnancy can also cause acne.
- Medications: Certain medicines, such as hormones, corticosteroids, halogen compounds, and lithium, can cause acne.
- Age: Individuals of all age groups can get acne, but it is more prevalent in teens.
The following factors do not cause acne but can exacerbate its symptoms:
- Diet: Certain studies show that consuming some foods may worsen acne. Investigators are still studying the role of diet as a cause of acne
- Stress
- Pressure from sports helmets, tight-fitting clothes, or backpacks
- Environmental factors, such as pollution and high humidity
- Squeezing or picking at scars
- Scrubbing the skin too hard
Decoding the Treatment for Acne
The approaches used to treat acne aim to manage the already existing lesions, prevent the development of new lesions, and reduce acne-related scarring. Medications can help eliminate some of the causes of acne, such as unusual clumping of cells in the follicles, bacteria, high levels of sebum, and inflammation. Healthcare professionals might recommend over-the-counter or prescription medications, both oral (pills) or topical (creams).
Topical medications, which an individual can apply to the skin, include:
- Over-the-counter products, such as benzoyl peroxide, which destroys bacteria and might reduce sebum production
- Antibiotics, which are generally used with other topical medicines
- Retinoids, derived from vitamin A, which aid in treating lesions and decrease inflammation. These agents also aid in preventing the formation of new acne and acne-related scarring
- Salicylic acid, which helps reduce whiteheads and blackheads and the shedding of the cells surrounding the hair follicles
- Sulfur, which aids in reducing whiteheads as well as blackheads
Topical medicines are available in many forms, including gels, lotions, creams, soaps, and pads. In specific individuals, topical medication might cause side effects such as burning, irritation of the skin, or redness.
For some individuals, the healthcare professionals might prescribe oral medications, such as:
- Antibiotics help slow down or inhibit the growth of bacteria and decrease inflammation. Healthcare professionals suggest antibiotics for moderate to severe acne, such as cystic acne.
- Isotretinoin, an oral retinoid, works through the bloodstream to help treat acne and open the pores. It is supplemented with other topical medicines, such as antibiotics, and help them enter the follicles to treat acne. Like topical retinoids, taking the medication orally can also help prevent acne formation and help with scarring.
- Hormone therapy, used primarily in females, helps stop the effects of male hormones on the sebaceous gland.
- Corticosteroids help lower inflammation from severe acne, including severe nodular acne.
People who do not benefit from oral or topical agents might need more intensive approaches, including:
- Laser and other light therapies
- Injecting corticosteroids directly into the impacted areas of the skin
- Superficial chemical peels that a healthcare professional suggests and applies to the area
- Filling acne scars with a substance to enhance their appearance
- Treating acne scars with tiny needles to aid in healing
- Surgical procedures to help treat and repair scarring
Healthcare professionals can recommend a treatment approach that can fade the existing dark spots. Using sunscreen outdoors is especially important for treating and preventing dark spots.
Teenage Years: Acne Woes!
During adolescence, teens’ bodies undergo hormonal changes that cause their skin to produce more oil. That oil mixes with skin cells and blocks pores, causing acne. Acne is not caused by stress, greasy foods, or chocolate.
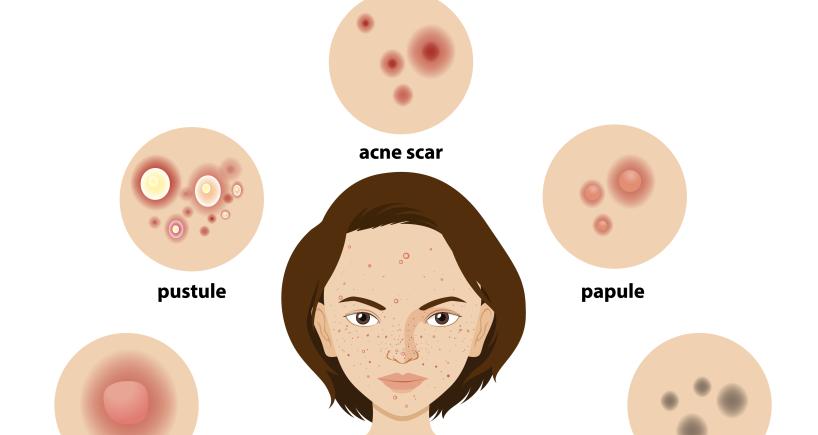
There are three major types of acne:
- Comedonal acne is the most prevalent type and is caused when pores get clogged and form blackheads and whiteheads.
- Inflammatory acne develops when the skin under the blackhead or whitehead becomes inflamed.
- The third and most severe kind is cystic acne. Often extremely painful, cystic acne is caused by an infection at the site of the clogged pore and can cause permanent scarring.
We have all gone through puberty and understand that acne might seem like the end of the world to teens. Parents should assure their children that acne is expected and that there is nothing to be embarrassed about.
Who Provides Acne Treatment?
The following healthcare providers might investigate and treat acne:
- Dermatologists are specialist medical professionals dealing with skin-, hair-, and nail-related ailments.
- Primary health care providers, including family doctors, internists, or pediatricians, can help too.
If a person experiences severe or persistent acne, they should seek medical attention. Physicians can recommend more vital prescription medicines.
Popular Searches
Hospitals: Cancer Hospital in Delhi | Best Heart Hospital in Delhi | Hospital in Amritsar | Hospital in Ludhiana | Hospitals in Mohali | Hospital in Faridabad | Hospitals in Gurgaon | Best Hospital in Jaipur | Hospitals in Greater Noida | Hospitals in Noida | Best Kidney Hospital in Kolkata | Best Hospital in Kolkata | Hospitals in Rajajinagar Bangalore | Hospitals in Richmond Road Bangalore | Hospitals in Nagarbhavi Bangalore | Hospital in Kalyan West | Hospitals in Mulund |
Doctors: Dr. Rana Patir | Dr. Rajesh Benny | Dr. Rahul Bhargava | Dr. Jayant Arora | Dr. Anoop Misra | Dr. Manu Tiwari | Dr. Praveer Agarwal | Dr. Arup Ratan Dutta | Dr. Meenakshi Ahuja | Dr. Anoop Jhurani | Dr. Shivaji Basu | Dr. Subhash Jangid | Dr. Atul Mathur | Dr. Gurinder Bedi | Dr. Monika Wadhawan | Dr. Debasis Datta | Dr. Shrinivas Narayan | Dr. Praveen Gupta | Dr. Nitin Jha | Dr. Raghu Nagaraj
Specialities: Heart Lung Transplant | Orthopedic |