Understanding Appendicitis: Causes, Symptoms, Risk Factors & Treatment
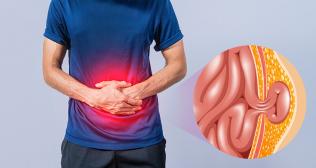
Appendicitis is a common but potentially serious medical condition that occurs when the appendix becomes inflamed. While appendicitis can affect individuals of any age, it most commonly occurs in people between the ages of 10 and 30. Understanding the causes, symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options for appendicitis is crucial for prompt diagnosis and effective management of this condition. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various aspects of appendicitis to provide you with the knowledge you need to recognize and address this condition.
Causes of Appendicitis:
The exact cause of appendicitis is not always clear, but it is often attributed to blockage of the appendix, leading to bacterial overgrowth and inflammation. The blockage can occur due to various factors, including:
Fecal matter: The appendix can become blocked by hardened stool, causing a buildup of bacteria and subsequent inflammation.
Enlarged lymphoid tissue: Infections or inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract can lead to the enlargement of lymphoid tissue in the appendix, contributing to blockage.
Foreign objects: Occasionally, foreign objects such as seeds, parasites, or even tumors can obstruct the appendix, triggering inflammation.
Symptoms of Appendicitis:
Appendicitis typically presents with the following symptoms, which may vary in severity:
Abdominal pain: The most common symptom of appendicitis is sudden and severe pain that starts near the navel and eventually migrates to the lower right abdomen. The pain may worsen with movement, coughing, or deep breathing.
Nausea and vomiting: Many individuals with appendicitis experience nausea, vomiting, or loss of appetite.
Fever and chills: Fever is common in cases of appendicitis, particularly when the inflammation is severe and accompanied by infection.
Changes in bowel habits: Some people with appendicitis may experience diarrhea, constipation, or difficulty passing gas.
Abdominal tenderness: The abdomen may be tender to the touch, particularly in the lower right quadrant.
It's important to note that not everyone with appendicitis will experience all of these symptoms, and the presentation can vary from person to person.
Risk Factors for Appendicitis:
While appendicitis can occur without any apparent cause, certain factors may increase the risk of developing this condition.
Age: Appendicitis is most common in individuals between the ages of 10 and 30, although it can occur at any age.
Gender: Men are slightly more likely to develop appendicitis than women. Family history: Having a family history of appendicitis or gastrointestinal disorders may increase the risk.
Dietary factors: A diet low in fiber and high in processed foods may contribute to the development of appendicitis by increasing the likelihood of fecal impaction.
Previous abdominal surgery: Individuals who have undergone abdominal surgery may be at a slightly higher risk of developing appendicitis due to the formation of scar tissue.
Treatment of Appendicitis:
The primary treatment for appendicitis is surgical removal of the inflamed appendix, a procedure known as an appendectomy. In most cases, appendectomy is performed laparoscopically, using small incisions and a camera to guide the surgeon. This minimally invasive approach typically results in shorter recovery times and less postoperative pain.
In some cases, particularly if the appendix has ruptured or if there are complications, an open appendectomy may be necessary. During an open appendectomy, the surgeon makes a larger incision in the abdomen to remove the appendix manually.
In cases where the appendix has already ruptured and caused infection in the abdomen (peritonitis), additional treatment may be required, such as antibiotics and drainage of abscesses.
Conclusion:
Appendicitis is a common abdominal emergency that requires prompt medical attention. By understanding the causes, symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options for appendicitis, you can take proactive steps to recognize the signs of this condition and seek appropriate care. If you or someone you know experiences symptoms suggestive of appendicitis, such as severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, or abdominal tenderness, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly to prevent complications and facilitate timely treatment.
Categories
Clear allMeet the doctor

- General Surgery | General Surgery
-
20 Years
-
1100