Understanding Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT)
What is CRRT, and how does it help?
Continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) is form of blood purification therapy which involves removal of excess fluids and uremic toxins from the patient’s blood. The process is slow, gentle and continuous – typically performed over 24 hours or more, enabling fluid homeostasis in patients experiencing AKI. The CRRT procedure mimics normal kidney function in healthy individuals. This article aims to help you understand the indications, benefits, types of CRRT, basis components of CRRT and other important topics.
Indications for Continuous Replacement Therapy
- Hemodynamically Unstable Patients: CRRT is primarily indicated for hemodynamically unstable patients - patients with unstable blood pressure and heart rate in intensive care units. Theoretically CRRT is less hypotensive than other procedures due to slower rate of fluid elimination during this procedure. Further, CRRT prevents a state of overload in patients that require extensive fluid management, including medications and parenteral nutrition.
- Brain edema: In critically ill patients with AKI, CRRT has been shown to cause fewer changes in terms of brain edema when compared to IHD.
- Sepsis and Multi Organ Failure: Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome occurs as a result of outpouring of inflammatory cytokines. With CRRT many of these mediators are removed from circulation, suggesting that CRRT has clinical benefit over IHD.
- Acute Lung Injury and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Early institution of CRRT for volume removal may be helpful in improving oxygenation and ventilatory parameters.
- Prevention of Radio Contrast Induced Nephropathy: Some studies found benefit of periprocedural CRRT in patients with CKD undergoing IV contrast studies.
- Drug Intoxication and Poisoning: CRRT has advantage in removing various poisons especially when plasma levels are low.
- Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO): CRRT may be performed on patients receiving ECMO.
- Infants and Children: CRRT can be used in infants and children with less hemodynamic change.
Benefits of Continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT)
- Continuous elimination of surplus metabolic waste products from the blood: CRRT machine enables continuous removal of uremic waste products which accumulate in the blood of patients with kidney failure. This helps prevent the build-up of toxins in the body thus preventing complications and organ damage.
- Restores normal electrolyte and acid/base balance: CRRT can help maintain normal electrolyte levels – level of sodium, potassium, and calcium, as well as normal acid/base balance, thus avoiding dangerous imbalances that can occur in patients with kidney failure.
- Maintains net neutral fluid balance: CRRT can help to maintain a net neutral fluid balance, which can prevent fluid overload or dehydration. This is especially important in critically ill patients who may have fluid imbalances due to other medical conditions.
- Provides for nutritional support irrespective of fluid restrictions: CRRT can provide nutritional support to patients who may be on fluid restrictions, allowing for the delivery of important nutrients without the risk of fluid overload.
- Allows for optimized drug administration: CRRT can help to optimize drug administration in patients with kidney failure, as many drugs are excreted through the kidneys and can accumulate in patients with renal impairment. CRRT can help to remove these drugs from the bloodstream, reducing the risk of toxicity.
Different types of Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
Continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) is used in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury and multi organ failure. Different types of CRRT used in clinical settings:
- Continuous Venovenous Hemofiltration (CVVH): In this technique, a large ultrafiltrate volume is passed across a convention or high-permeability membrane.
- Continuous Venovenous Hemodialysis (CVVHD): In this technique, blood is passed through a filter, and waste products are removed through diffusion. Replacement fluid is then infused to replace the removed fluid.
- Continuous Venovenous Hemodiafiltration (CVVHDF): In this technique, diffusive clearance removes solutes and toxins from the patient’s circulation. It combines convection and diffusion to remove fluid and solids through an efficient hemodiafilter.
- Slow Continuous Ultrafiltration (SCUF): This technique involves the removal of excess fluid from the body through ultrafiltration without the addition of replacement fluid.
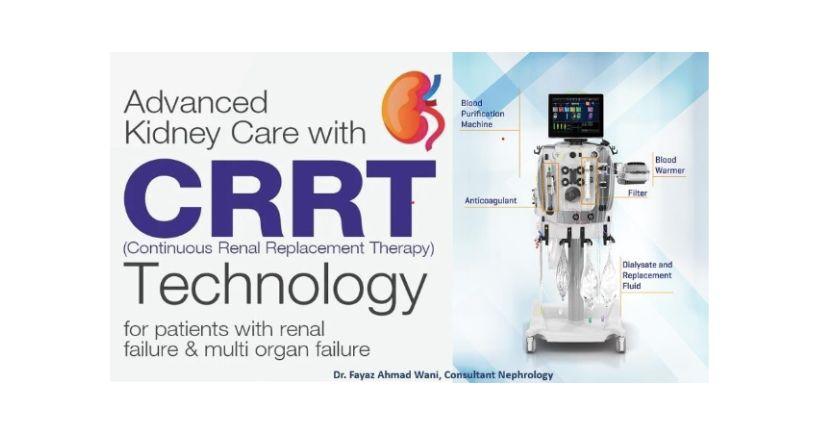
Basic Components of CRRT
The six medical products that are required to perform CRRT on a patient are:
- Blood purification machine: The machine pumps the blood, controls the rate of blood flow and includes software to safely monitor therapy delivery
- Dialysate: A fluid that carries toxins away from the filter
- Replacement fluid: A specialized, sterile fluid also used to flush toxins from the body but also to replace electrolytes, other blood elements and volume lost during the filtration process
- Filter: Machine component that removes fluid and uremic toxins
- Anticoagulation method: A type of drug that helps the blood flow through the system, lessening the likelihood that the blood will clot in the filter
- Blood warmer: Efficiently maintains a patient's blood temperature during blood purification therapy
Does all dialysis work the same for AKI?
Many factors influence the decision on what type of therapy is best for AKI. While some patients may undergo complete recovery, for others, AKI could complicate existing chronic kidney disease (CKD), develop into CKD, or cause irreversible loss of kidney function or end-stage renal disease.
Difference between CRRT and dialysis
In hemodialysis, waste filtration is done quickly and completed in a few hours. But in CRRT, due to technical differences from routine hemodialysis, it happens slowly, can be performed continuously around the clock, and results in more stable blood pressure during the procedure.
Conclusion
CRRT procedure is a safe and effective procedure for acute kidney injury patients. It is preferred over other forms of dialysis in certain situations, such as for patients with hemodynamic instability or those who require precise control over fluid and electrolyte balance.
CRRT is a complex and highly specialized procedure that requires close monitoring and adjustments to ensure optimal patient outcomes. The treatment is performed by a team of healthcare professionals, including nephrologists, nurses, and dialysis technicians, who work together to provide the best possible care for the patient.
Popular Searches :
Hospitals: Cancer Hospital in Delhi | Best Heart Hospital in Delhi | Hospital in Amritsar | Hospital in Ludhiana | Hospitals in Mohali | Hospital in Faridabad | Hospitals in Gurgaon | Best Hospital in Jaipur | Hospitals in Greater Noida | Hospitals in Noida | Best Kidney Hospital in Kolkata | Best Hospital in Kolkata | Hospitals in Rajajinagar Bangalore | Hospitals in Richmond Road Bangalore | Hospitals in Nagarbhavi Bangalore | Hospital in Kalyan West | Hospitals in Mulund | Best Hospital in India | | Cardiology Hospital in India | Best Cancer Hospital in India | Best Cardiology Hospital in India | Best Oncology Hospital In India | Best Cancer Hospital in Delhi | Best Liver Transplant Hospital in India
Doctors: Dr. Rana Patir | Dr. Rajesh Benny | Dr. Rahul Bhargava | Dr. Jayant Arora | Dr. Anoop Misra | Dr. Manu Tiwari | Dr. Praveer Agarwal | Dr. Arup Ratan Dutta | Dr. Meenakshi Ahuja | Dr. Anoop Jhurani | Dr. Shivaji Basu | Dr. Subhash Jangid | Dr. Atul Mathur | Dr. Gurinder Bedi | Dr. Monika Wadhawan | Dr. Debasis Datta | Dr. Shrinivas Narayan | Dr. Praveen Gupta | Dr. Nitin Jha | Dr. Raghu Nagaraj | Dr. Ashok Seth | Dr. Sandeep Vaishya | Dr. Atul Mishra | Dr. Z S Meharwal | Dr. Ajay Bhalla | Dr. Atul Kumar Mittal | Dr. Arvind Kumar Khurana | Dr. Narayan Hulse | Dr. Samir Parikh | Dr. Amit Javed | Dr. Narayan Banerjee | Dr. Bimlesh Dhar Pandey | Dr. Arghya Chattopadhyay | Dr. G.R. Vijay Kumar | Dr Ashok Gupta | Dr. Gourdas Choudhuri | Dr. Sushrut Singh | Dr. N.C. Krishnamani | Dr. Atampreet Singh | Dr. Vivek Jawali | Dr. Sanjeev Gulati | Dr. Amite Pankaj Aggarwal | Dr. Ajay Kaul | Dr. Sunita Varma | Dr. Manoj Kumar Goel | Dr. R Muralidharan | Dr. Sushmita Roychowdhury | Dr. T.S. MAHANT | Dr. UDIPTA RAY | Dr. Aparna Jaswal | Dr. Ravul Jindal | Dr. Savyasachi Saxena | Dr. Ajay Kumar Kriplani | Dr. Nitesh Rohatgi | Dr. Anupam Jindal
Specialties: Heart Lung Transplant | Orthopedic | Cardiology Interventional | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | Onco Radiation | Neurosurgery | Interventional Cardiology | Gastroenterologist in Jaipur | Neuro Physician | Gynecologist in Kolkata | Best Neurologist in India | Liver Transfer | Best Cardiologist in Delhi
Categories
Clear allMeet the doctor

- Nephrology | Nephrology
- Organ Transplant | Kidney Transplant
- Paediatrics | Paediatric Nephrology
-
8 Years
-
700