Hives Allergy: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
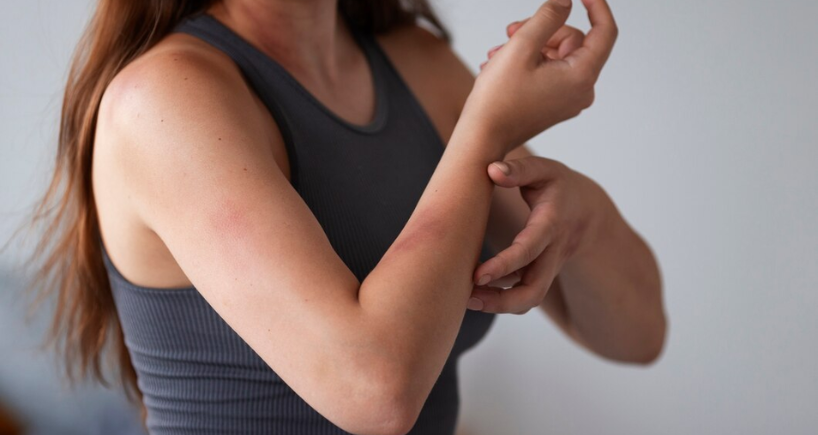
Hives or urticaria are colored bumps on the skin surface. An allergic reaction causes hives due to exposure of the body’s immune system to an allergen. They can cause burning or stinging sensation and range from small to big. Based on the duration of the hives, they are categorized as
Acute hives occur for a shorter duration, lasting less than six weeks.
Chronic hives, even though not permanent, occur almost twice a week and last longer than six weeks.
What causes Hives allergy?
Hives allergy is the body’s immune response to the allergen that comes into contact with the body’s immune system. The allergen can be in the food, medicines, drinks, contact with any allergens, or autoimmunity. Mast cells are the immune cells in the skin that release chemicals called histamine. Histamine is a chemical the body produces that triggers allergic reactions in the body. Excess production of these chemicals starts Hives.
- Acute hives are mostly allergic reactions to viral infections, food, drugs, environmental allergies, or insect bites. Infections, stress, and physical pressure can also cause acute hives. Foods that trigger acute hives are chocolate, raw eggs, fish, fresh raw berries, nuts, tomatoes, food additives, and preservatives. Other include painkillers, blood pressure drugs, and milk.
- Chronic hives are mainly associated with autoimmunity. Specific diseases, exposure to cold, sunlight, or water, or spontaneously can trigger them. Establishing a cause for chronic urticaria is usually difficult; it can also affect systemic organs like the heart, lungs, and digestive system.
- Physical urticaria is hives due to skin stimulation by pressure exercise, sweating, or vibration. They occur on the location of the skin, remain for some time, and go for a few hours. This can also happen due to stroking or scratching of the skin, called dermatographism or stress hives.
Symptoms:
Hive symptoms have individual variations. They may also vary depending on the type and the allergen exposure.
- They may appear for a few minutes and may exist for years.
- They are raised, swollen, red, or skin-colored bumps on the skin.
- Pressure on the hives whitens them, and they become pale. This is called blanching.
- Skin feels itchy, and the intensity increases at night
- Puffiness under the skin due to swelling is called angioedema and can be seen on the lips, eyes, and inner part of the throat.
- Chronic hives also have similar symptoms but can take different shapes and sizes. They reappear frequently every few days and are seen when exposed to heat, stress, or exercise.
Hives treatment:
Physical examination, skin allergy tests, and specific blood tests diagnose hives. They are treated by the following:
- Medications like antihistamines are prescribed to reduce the severity and itching. These can be given as pills to swallow, to apply to the skin, or through an intravenous bloodline. These include diphenhydramine, cetirizine, fexofenadine, and many other classes of medications. Steroids are also prescribed in cases that do not respond to antihistamines.
- Allergy injections are prescribed to chronic hives patients who produce large quantities of immunoglobulins and histamines that trigger allergies. These injections are taken monthly to block the increased production.
- In case of life-threatening allergic reactions like anaphylaxis, epinephrine injections are prescribed to control the allergic reactions.
At-home Hives treatment:
An individual with hives should take care of the following:
- Cool baths to reduce the itch
- Loose-fitting clothes
- Cold compresses over the hives
Hives prevention:
Hives can be prevented by doing the following:
- Identify and avoid foods that trigger allergic reactions
- Beware of airborne allergens
- Relax the body when doing extreme exercises that can produce severe sweating.
- Avoid sudden changes in the temperature.