Parkinson’s Disease: A Glimpse into A Common Neurological Disorder
What is Parkinson’s Disease?
Parkinson’s disease is a neurological disorder that usually occurs with advancing age. This is usually a progressive disorder which is due to a decrease in a neurotransmitter in the brain called Dopamine.
It usually affects people in their late 60s, however in India, Parkinson’s disease starts a little earlier around the age of 50 in comparison to the Western world. Around 10 million people are living with Parkinson’s disease in the world and around 50-60 persons per 100,000 population suffer from Parkinson’s Disease. This disease is more common in males as compared to females.
What causes Parkinson’s Disease?
There are no definite reasons or causes of Parkinson’s Disease.
Around 10-20 % of patients with PD can have some genetic association. Several genes are associated with it. However, most of the patients will not have another family member suffering from the same disease.
α synuclein is a protein that is found in the brain, abnormal accumulation of this protein in areas of the brain leads to a decrease in neurotransmitters.
Exposure to pesticides and well water has been found to increase the risk of disease.
However, the role of environmental toxins and pollution can’t be ignored, there has been an increase in the incidence of disease which is probably due to increasing environmental toxins.
Overall, there is no clear external factor that can be avoided to decrease the risk.
How do we recognize symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease?
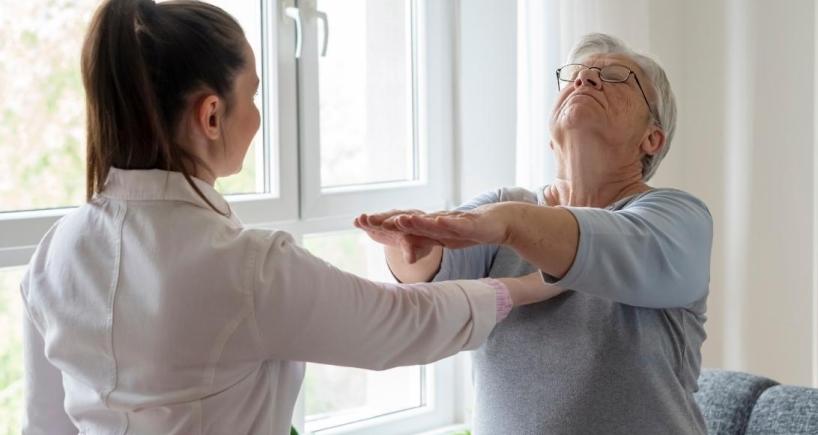
Tremors: The most common symptoms are Tremors or shaking of limbs. Tremors usually occur in one side of the body, they are usually minimal, and many times ignored by the patients. There can be problems in writing, wearing clothes, shaving, and cooking which many times patients consider to be non-specific reasons. Gradually, the tremors progress and can be visible to others.
Slowness: Patients usually are not able to recognize these symptoms. However, their family members observe that they have become clumsy, and are taking more time in day-to-day work like bathing, and shaving, their speed of walking decreases in comparison to peers. At times, they appear to be a little dull and not as active as they usually used to be.
Rigidity or Stiffness: There is a feeling of heaviness/tightness in arms or legs, movements become difficult, and there is difficulty in turning in beds.
These are the usual symptoms, however, as the disease progresses, patients can have imbalance, urinary problems, and memory issues.
Many patients have problems like a decreased sense of smell, restlessness in their legs, and constipation which can be present for years before the onset of tremors.
How do we diagnose Parkinson’s Disease?
Diagnosis is still clinical based on patient symptoms and examination. The advice of an expert neurologist who is dealing with movement disorder patients is a must for proper treatment.
Few investigations like MRI and advanced imaging like SPECT can be helpful in a certain number of patients.
Few advanced tests that use blood or skin samples are in research and will be available in the coming years for diagnosing Parkinson’s disease.
Can we cure Parkinson’s Disease?
Parkinson’s disease is not curable in exact terms, symptoms occur when already around 50 % of neurons producing Dopamine have been lost. However, there are several medications and procedures available.
Medications: Dopamine replacement is key to treatment. L-Dopa a commonly used drug helps in the improvement of symptoms significantly; other similar drugs are useful in different stages of disease. However, after 5-10 years of treatment, these medicines become less effective and can lead to side effects.
Surgery: Brain Pace Maker or Deep Brain Stimulation is a treatment for PD patients and is available for more than 25 years. A lead is placed in the brain connected to an external device which gives regular pulses to the brain. DBS is an effective treatment, especially in patients who are not responding to medicines.
Other treatment options like the placement of a tube in the intestine, ultrasound-guided treatment of a part of the brain, and inhalational dopamine are advancements that are available.
Can we prevent Parkinson’s Disease?
Parkinson’s disease cannot be prevented but there is large role of exercise, diet and lifestyle in reducing the chances of getting the disease and slowing down its progression.
Exercise: Exercise releases chemicals that help in making new connections in the brain. Exercise has been found to slow down disease progression. Music therapy and dance therapy are useful in maintaining the functionality of patients.
Diet: A balanced diet, rich in antioxidants and nutrients is key for healthy life including prevention of Parkinson’s disease.
Parkinson’s disease effects both young and old, recognition of early symptoms is important for proper treatment. Lifestyle modifications and treatment can help us in decreasing the burden of disease and leading a normal life with Parkinson’s disease.
Categories
Clear allMeet the doctor

- Neurology | Neurology
-
15 Years
-
1200